half life formula for zero order reaction
In order to solve for half life of second order reactions we need to remember that the rate law of a second order reaction is. For the reaction given as A B A is reactant and B is a product Rate -dA dt kA0 -dA dt k dA -k dt Now Integrating both sides we get.

Half Life Expressions Chemistnate
The formula for half-life in chemistry depends on the order of the reaction.

. Using the integrated form of the rate law we can develop a relationship between zero-order reactions and the half-life. In this instance the half-life is decreased when the original concentration is reduced to 10 M. Equations for Half Lives.
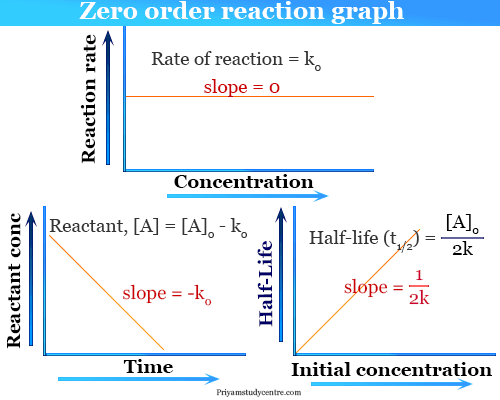
The rate constant for a zero-order reaction is measured in molL -1 s. The half-life for a zero-order reaction is inversely proportional to its rate constant. Graphical relations and half lives.
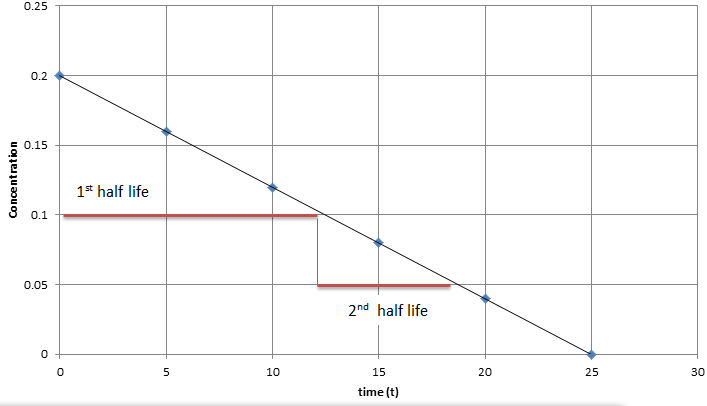
When t t ½ that is the half-life of the reaction completed the concentration of the reactant A A2. Ii The formula to calculate half life period t12. Substituting t t12 and A t ½ A 0 in the zero-order integrated rate law yields.
In the case of a zero-order reaction the rate of reaction depends on the zeroth power of the concentration of reactants. The half-life of a zero-order reaction the formula is given as t12 R02k The half-life of a first-order reaction is given as t12 0693k The half-life of a second-order reaction is given by the formula 1kR0. The mathematical expression that can be employed to determine the half-life for a zero-order reaction is t12 R 02k For the first-order reaction the half-life is defined as t12 0693k And for the second-order reaction the formula for the half.
Slope k 131106 molLs slope k 13110 6 mol L s Figure 3. K 12t 1a-x 2-1a2 PSEUDO-ZERO ORDER REACTION In solid state may drug decomposes by pseudo zero order ie. Answer i Arrhenius equation is k AeE aRT or lnk lnA RT E a.
What is the equation for the half-life of a zero-order process. The zero order reaction rate law can be represented as ratek where k is denoted as the constant rate. Converting a half life to a rate constant.
For a zero order reaction A products rate k. The Half-Life of a Reaction. A -kt c Where c constant of integration At time t 0 A A0.
Since this is a zero-order reaction the half-life is dependent on the concentration. Determining a half life. Correct option is C For zero order reaction the half life period t 12.
The rate constant for the reaction can be determined from the slope of the line which is equal to -k. T ½ 1 k A o Top. Because this equation has the form y mx b a plot of the concentration of A as a function of time yields a straight line.
For first-order reaction the half-life period t 12. The half-life of a Zero-th order reaction is t A0 2kHere I derive this from the Integrated Rate LawAsk me questions. 11 A A o k t Substitute 12 1 2 A o A o k t 1 2 Solve for t 1 2 13 t 1 2 A o 2 k.
As the concentration decreases the half-life of the zero order reaction also decreases. 245 1 A k t 1 A 0 As in zero-order and first-order reactions we need to isolate t 1 2 when A A o 2 Substituting into Equation 245 2 A 0 k t 1 2 1 A 0 k t 1 2 1 A 0. T ½ A o 2k For a first order reaction A products rate kA.
What is the zero order rate law. However the half-life of a zero-order reaction increases as the initial concentration increases. Ii The formula to calculate the half-life period of zero order reaction.
Second Pseudo 1st order reactions differential form Integrated rate law and Half-life equation. TRA3C4 EK Transcript The integrated rate law for the zero-order reaction A products is A_t -kt A_0. Rate eqn third order reaction is as follows.
T ½ 0693 k For a second order reaction 2A products or A B products when A B rate kA 2. Thus for zero order reaction the half life period is directly proportional to the initial concentration. For a first order reaction t½ 0693 k and for a second order reaction t½ 1 k Ao.
The decomposition of NH 3 on a tungsten W surface is a zero-order reaction whereas on a quartz SiO 2 surface the reaction is first order. Half life in zero order reaction Half life means 50 percent of reactants disappear in that time interval. Here k is the rate constant A is the preexponential factor Ea is the energy of activation R is the ideal gas constant and T is absolute temperature.
Reaction between drug and moisture in solid dosage form. From the slope of the line for the zero-order decomposition we can determine the rate constant. The equation is t 12 R 0 2k.
Therefore A2 k 0 t ½ or t ½ A2k. The zero order kinetic rate law can be shown as below A A 0 k t ------ 1 Where A current concentration A 0 initial concentration k reaction constant t time To determine half-life dividing equation 1 by 2 t 12 A 0 2 t. The half-life equation for a first-order reaction is t12ln2k t 1 2 ln 2 k.
For a zero order reaction the formula is t½ Ao 2k. Half-life or t½ is the time that elapses before the concentration of a reactant is reduced to half its initial value.
Zero Order Reaction Definition Examples Formula

What Is The Half Life In Seconds Of A Ze Clutch Prep

Half Life Of A Zero Order Reaction Is 250sec T75 T100 Of The Reaction Respectively In Sec Are Edurev Neet Question

Half Life Expressions Chemistnate

Half Life Of Zero Th 0th Order Reaction Derivation Youtube

Zero Order Reactions Chemistry Class 12 Iit Jee Main Advanced Neet Aipmt Askiitians Youtube